Geofence Application: Testing the GPS
Paring the Bluetooth devices
In order to pair the Bluetooth GPS and Bluetooth-RS232 we need to configure the two to pair. For the particular device I have this is achieved by using the setup utility provided.
Once the MAC and pin have been programmed into the Bluetooth adapter this can be connected to the DB9 crossover cable and testing can begin.
Serial Proxy
In order to check that the WiFire can read data from the GPS we will create a simple sketch that repeats all data it receives from the RS232 shield out on its Serial output. This version can be found here and seen below.
/* We want to map pins 5 and 7 to Serial2 (for RX and TX respectively).
Serial2 uses using the WiFire's UART6 and both pin 5 and 7 support
being mapped to the relevant peripheral (U6RX and U6TX).
Note that pin 5 is chosen (actually it is already mapped to U6RX
by default) as it is a 5v tolerant pin, so the UART chip connected
may operate at 5v levels. It is also necessary that the UART chip
accepts 3v3 as a logic HIGH as this is the logic HIGH provided by
pin 7.
For this example the MAX232 is used, which operates at 5v but
accepts 3v3 as HIGH
*/
#define SERIAL2_RX_PIN (5)
#define SERIAL2_TX_PIN (7)
// The GPS module we will be using uses a 9600-baud RS232 connection
#define GPSBaud (9600)
void setup()
{
// use the same baud rate as the boot console so that we
// don't have to change the serial connection baud rate
Serial.begin(115200);
// We are not reading from Serial and don't mind sharing
// it with the FlowCloud libraries
g_EnableConsole = true;
g_EnableConsoleInput = true;
Serial.print("Bringing up GPS serial connection... ");
// remap our desired RX and TX pins to U6 (Serial2)
mapPps(SERIAL2_RX_PIN, PPS_IN_U6RX);
mapPps(SERIAL2_TX_PIN, PPS_OUT_U6TX);
// Start up Serial2
Serial2.begin(GPSBaud);
Serial.println("OK!");
Serial.println();
Serial.println();
}
void loop()
{
while (Serial2.available() > 0)
{
Serial.write(Serial2.read());
}
}If we upload this and ensure that the GPS is on and has signal we can see the following in out Serial Monitor (making sure we are operating in 115200 baud).
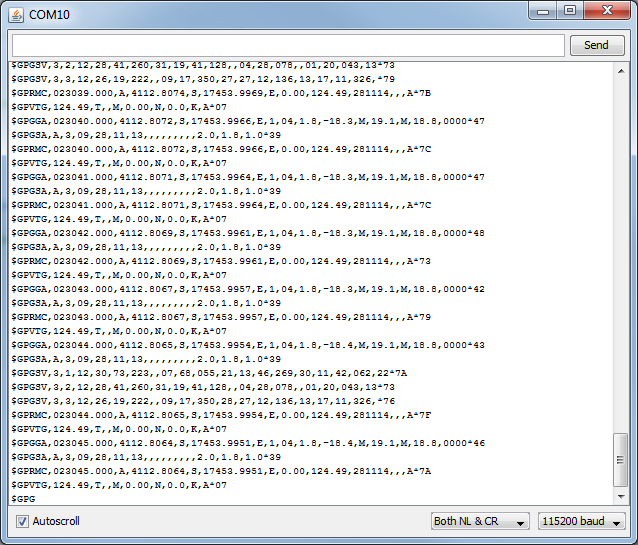
Now that this is working, it's time to do something with our data.